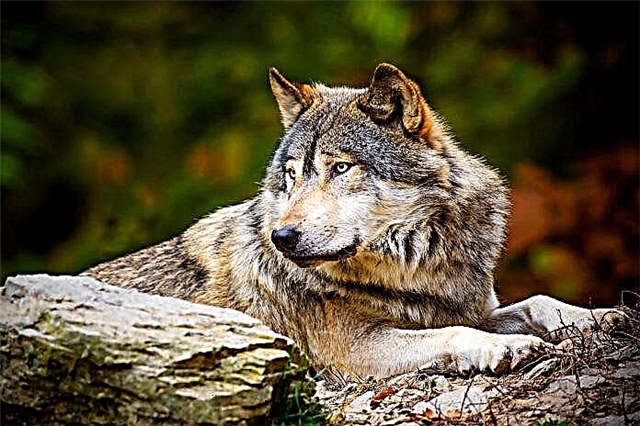
More recently, wolves could be found in different places on our planet - both in Eurasia and in America. What subspecies of the wolf are still found, where do they live, and what kind of lifestyle do they lead?
Wolf - a brief description of the species
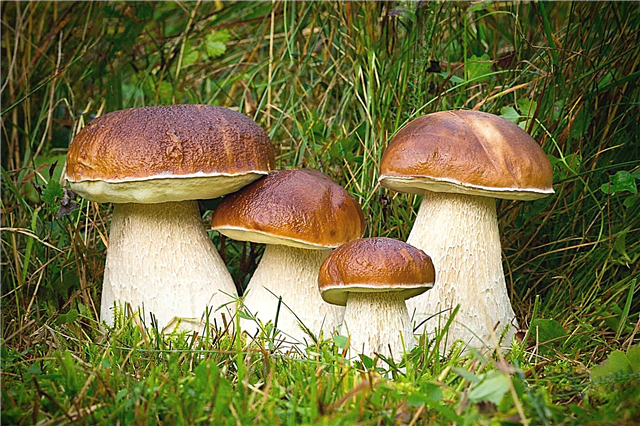
A wolf is a predatory animal from the mammalian class. Multiple studies show that this is the ancestor of the dog. More recently, they could be found in different places on our planet - in Eurasia, America.
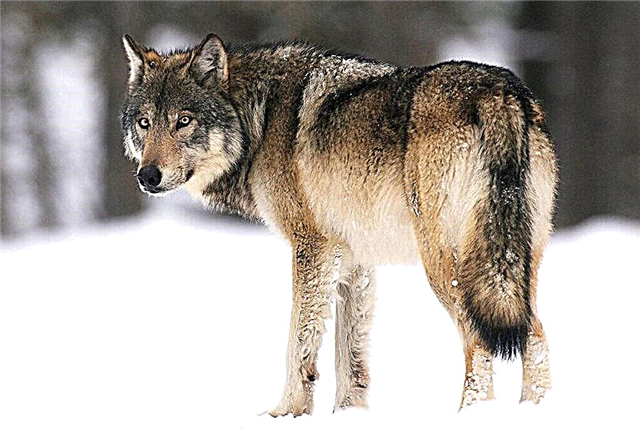

Leads a pack life. In the ecosystem plays a critical role. For example, in the tundra, steppes, a flock destroys sick animals, "updating" the natural gene pool.
Appearance of the wolf
The appearance of the wolf may vary. This is affected by the climate where the animal lives and what it eats. The wolf is considered one of the largest representatives of the family. The inhabitants of various natural zones have adapted to environmental conditions.
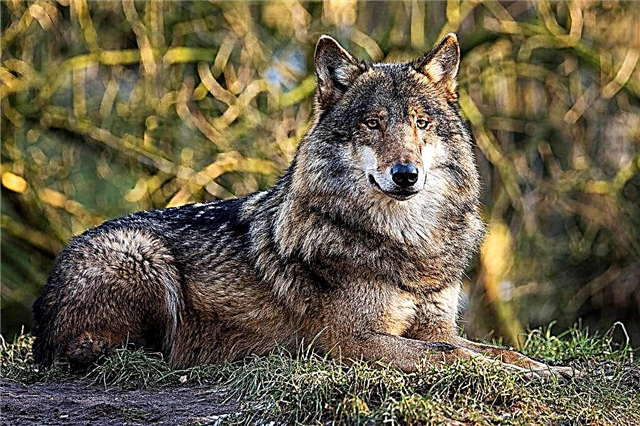

Interesting fact: The Arabian Wolf (canis arabs) is the smallest subspecies and its weight does not exceed 15 kg.
Height and weight
The male, as a rule, is 20% larger than the she-wolf. Height - 66-96 cm at the withers, body length - 102-147 cm, tail - 33-51 cm. Weight on average - 27-45 kg, but individuals weighing 80 kg were found.
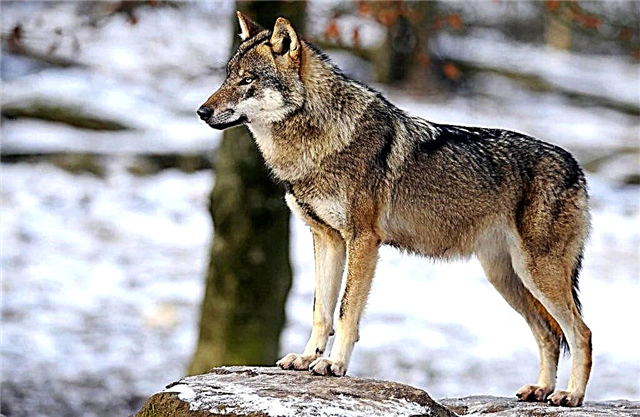

Skin colors
The coat is medium length. The color can be black, white and with different shades - cream, yellow, brown, gray, etc. On the stomach, usually the fur is lighter, and on the back - darker.
A short, smooth coat of light color is located on the upper part of the muzzle, forehead and ears. Even lighter wool on the neck. On legs, legs grows a short loose fur.
On the tail of the beast - thick, long and fluffy fur. Its color depends on the main color of the individual: from below - light, from above - darker. Most often, a small wolf cub is born with dark hair, which changes as it grows. There are no albino wolves.
Eyes of the gray wolf
Puppies have dark blue eyes that gradually brighten. Within 6-10 weeks, the color gradually forms and becomes permanent. In an adult wolf, golden or amber eyes are most often found. Different shades are also possible. Blue-eyed predators are often not purebred.
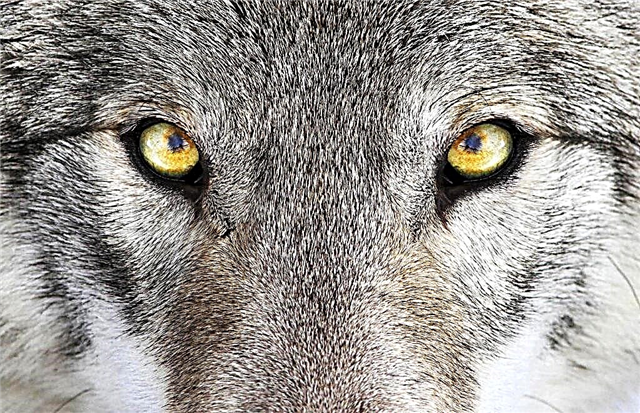

Vision of a gray wolf
Some researchers believe that these animals have developed myopia, since there are no sufficient depressions on the retina that are responsible for focusing objects at long distances.
Probably wolves suffer from color blindness (partially). In the eye of the beast there are only blue and red receptors. The tests that were conducted showed that among several colors, wolves choose red and yellow.

Wolves have good peripheral vision and, due to this, quickly respond to any movements. The high ratio of photoreceptors (cones and rods) allows you to see well at night.
Wolf ears
Ears are triangular in shape, slightly rounded on top. The back side has little hair, which can not be said about the inside - there the fur is darker, longer. Ears can move regardless of each other, cling to the head and rotate. Due to the rotation of the ears, wolves can determine the direction of sound.

Habitat
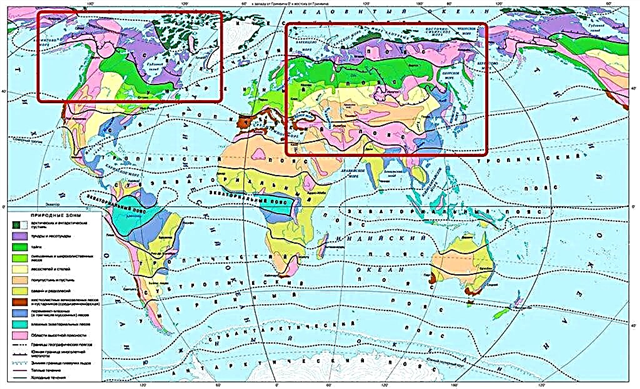
Before, the beast could be found almost everywhere in the world, but now the habitat has greatly narrowed due to humans and other factors. In the modern world, it is found mainly in the Northern Hemisphere. Distributed everywhere in the Russian Federation, except for Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands.
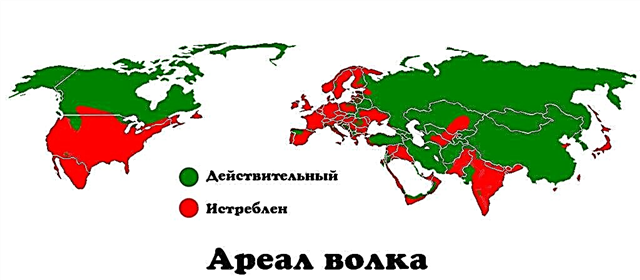
Habitat
Animals can occupy different natural zones: forests, tundra, steppe, etc. In the mountains they live at an altitude of 3000-4000 m. In the tundra, steppes, wolves can move after a herd of artiodactyls.
Thickets of bushes, caves and other places are needed for the lair - a place where puppies are bred. Near their home, wolves rarely go hunting, most often they go 7-10 km.
What does a gray wolf eat?
The wolf is an active predator. Large animals become its targets.The diet depends on the occupied natural zone.
So, wolves that live in the steppes or deserts feed on antelopes. Residents of the forest-steppe prey on deer, roe deer, wild boars and moose. For tundra predators, reindeer are the basis of the diet.
It is noteworthy that sometimes predators, being close to the household, attack livestock: horses, sheep, cows. In the absence of larger prey, small animals are hunted: mice, hares, raccoons. Busting bird nests, stealing eggs and chicks.
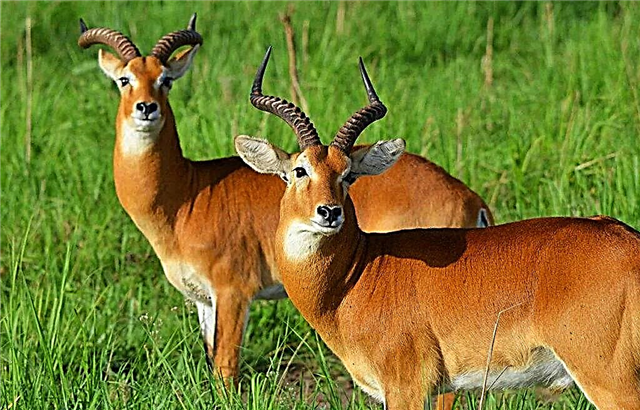

To quench their thirst in hot southern conditions, wolves can eat berries and fruits. Hungry individuals feed on any food they can find - right down to frogs, small snakes, and beetles.
Interesting fact: exhausted by thirst, wolves can eat watermelons. At the same time, they gnaw the fruits until they find ripe.
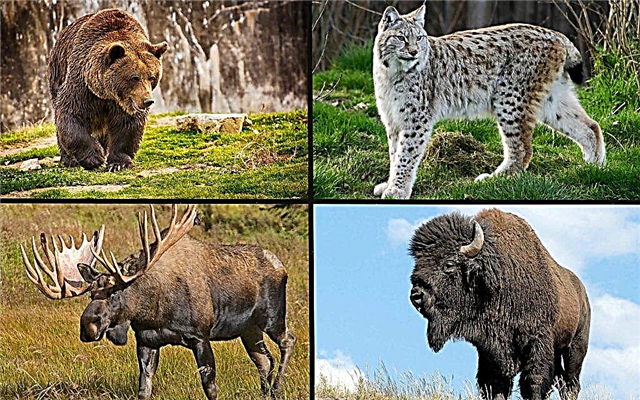
Natural enemies of the gray wolf
These predators have quite a few natural enemies: bears, lynxes, bison, moose. Wolves get most injuries during hunting or accidental skirmishes with no less aggressive animals. However, the greatest danger to them is people who are engaged in hunting, poaching.

How many wolves live?
In nature, predators live less than in captivity. So, on average, life expectancy in the natural habitat is 6-8 years. Occasionally, individuals live up to 13 years. In reserves and other protected areas they are 2 times longer, about 16-17 years.

Population and species status
In the past, the species was widespread in Eurasia, America. Now their population has declined significantly. The whole blame is human activity, changing environmental conditions. In some regions, the species is threatened with extinction. More or less stable populations remained in the northern regions of Eurasia and America.
The exact abundance of the species is problematic. Some subspecies are considered extinct, but in general the number of individuals does not allow the predator to be included in the Red Book. Therefore, officially it is considered a species under the least threat of extinction.
Data on the number of wolves in some countries for 1998:
- Alaska - from 6000 to 8000;
- Canada - 60,000;
- Russia - 30,000;
- Kazakhstan - 9000;
- China - 6000;
- Belarus - 2000;
- India - 1600;
- Latvia - 900;
- Estonia - 500.
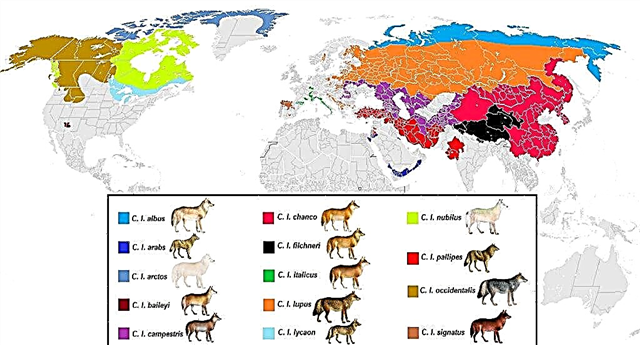
Types of wolves
It is believed that the wolf has more than 10 subtypes. Scientists also identify several ancient extinct species: terrible, Kenai, Newfoundland, Tasmanian marsupial, Japanese, Mogollan mountain, Manitoba, Hokkaido, Florida.
The confusion arises from the fact that there is a genus of wolves, an ordinary wolf species, and also its subspecies. In addition, sometimes in the names of animals that belong to other genera, the word "wolf" also appears. For example, the red wolf is the only representative of its unique genus and is not related to other wolves.
Consider only the subspecies of the wolf that currently exist, which include, but not limited to, dogs (domesticated) and dingoes.
Tundra
It is found in our country in the natural zones of the tundra and forest-tundra. In 2nd place in size after the polar subspecies. The location depends on how the deer are placed - the main prey. The subspecies is poorly understood. It features light, long and dense coat. Weight - up to 50 kg.
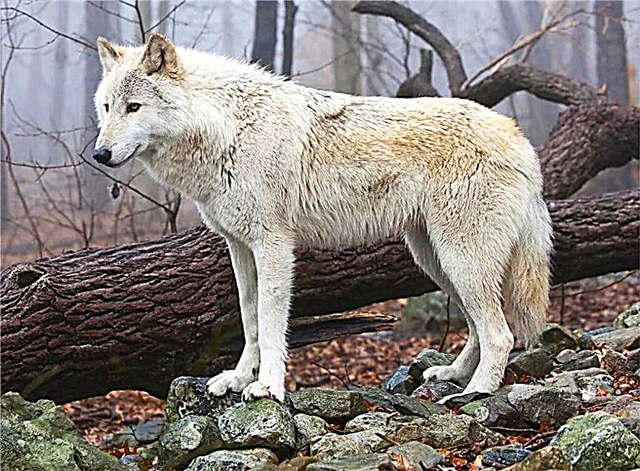

Interesting fact: The tundra wolf and she-wolf live separately all the time except for the mating season. Moreover, they easily manage to find each other every time.
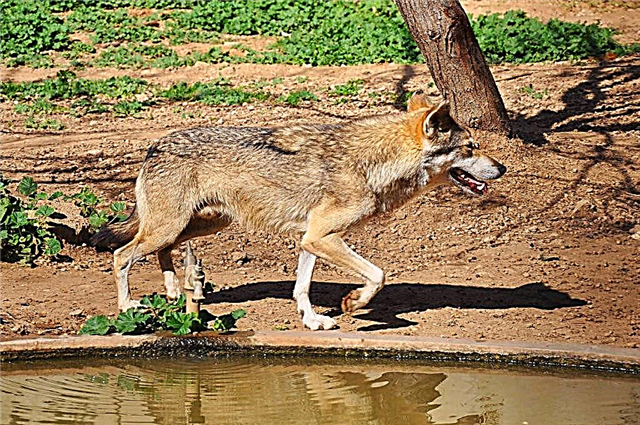
Arabian
It was formerly distributed on the Arabian Peninsula. Now found only in some areas. Small subspecies, adapted to life in the desert. The average weight is about 18 kg, the height at the withers is 66 cm. It has disproportionately large ears, due to which the heat emanating from the body is dissipated.

Melville Island
It is found on the Arctic islands of North America and in Greenland. A subspecies of medium size: height - up to 79 cm, weight - about 45 kg (occasionally individuals gain 80 kg of weight). Miniature ears help keep you warm.Melville wolves live in packs of up to 10 individuals.

Mexican
It is found in North America. It has a gray or dark color. Medium-sized individuals: about 70 cm tall and weighing 23-41 kg. Since 1960, it has been forbidden to destroy Mexican wolves in order to restore their population.
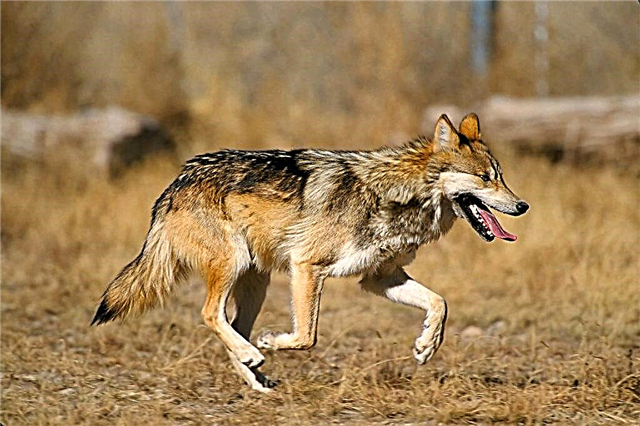

Steppe
The second name is the desert wolf. It is found in the desert zones of Central Asia. The coat is short, light gray with yellowish brown spots. The subspecies is poorly understood. The total number is considered low.

Interesting fact: female is fully engaged in the upbringing of the wolf The offspring usually consists of an odd number of puppies. At the same time, the she-wolf leaves only the strongest babies with the expectation that there will be enough milk for feeding.
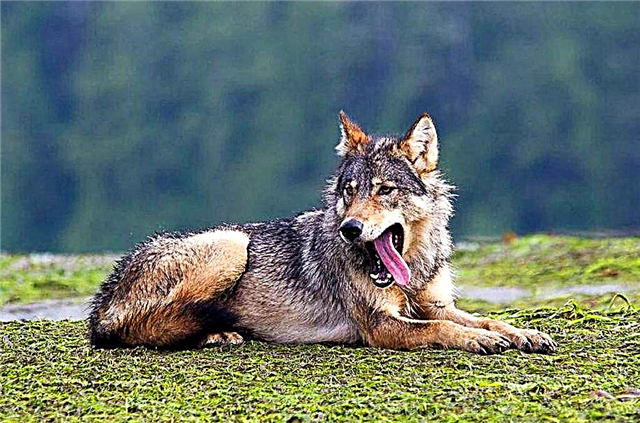
Vancouver Island
An endemic subspecies found only on Vancouver Island. It features gray or black coat color. Although white individuals are known. Lives in large schools (up to 35 individuals). It feeds mainly on artiodactyl animals. Tries to avoid people.

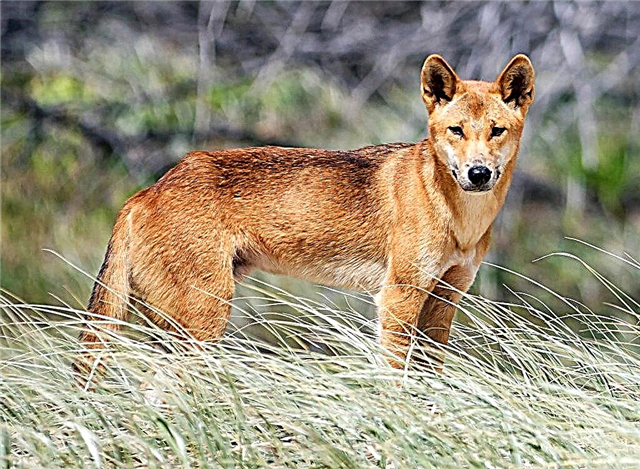
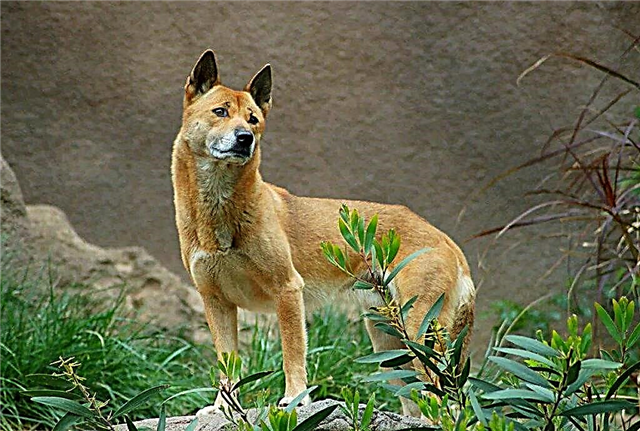
Dingo
Secondarily feral dingo dog has a red color, which can take on different shades. The dimensions of individuals vary greatly: weight - from 9 to 19 kg, height - from 47 to 67 cm. Females are much smaller than males. Most dingo is common in Australia. Leads a nocturnal solitary lifestyle.

Dog
As for domestic dogs, there is still a debate about the origin. In the current scientific classification, they are considered subspecies of the gray wolf. The variety of dog breeds is huge and some of them existed in antiquity. The breeds differ in all respects: appearance, character, purpose, etc. There are also purebred breedless dogs.

New Guinea Dog Singing
A wild dog found in the forests of New Guinea. It looks like a dingo and an ordinary dog at the same time. The New Guinean subspecies is considered not as fast and hardy as a domestic dog, but more flexible and dexterous. Dimensions are small: weight - about 12 kg, height - 40 cm.

Interesting fact: New Guinean dogs make unique sounds that are not common to other subspecies. Their howl resembles the sounds made by whales, or bird singing.
Hudson
A small subspecies that lives near the Hudson's Bay (in the northern and western parts). In summer, it has a light color, and in winter it becomes completely white. Moves after the deer.

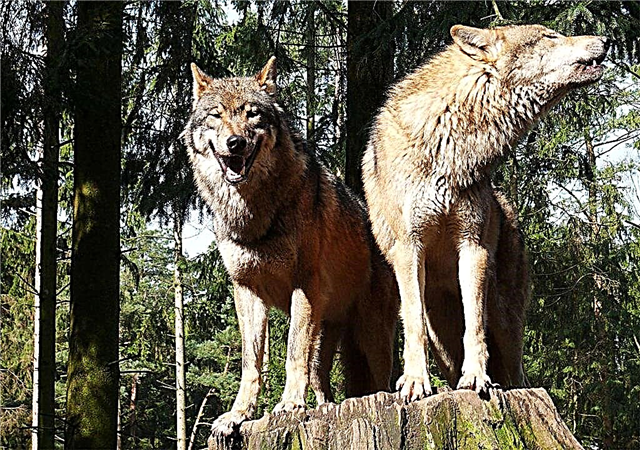
European
The most common subspecies of the gray wolf. It has a short and thick coat of a grayish hue with spots of red, white, black. Dimensions depend on the habitat of individuals. On average, European wolves grow up to 76 cm in height and gain about 70 kg.

Oriental
Distributed in Canada. Average height - 80 cm, weight - 40 kg. Females are smaller and lighter. The color of the eastern (or North American) wolf includes shades of gray, yellow, brown and black. A subspecies lives in a small flock.
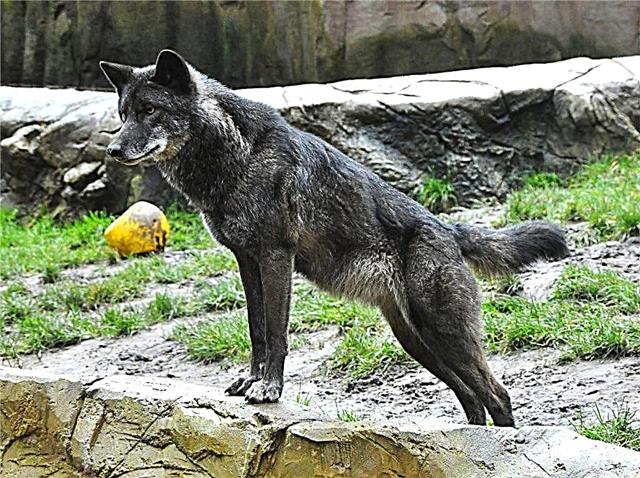

Wolf of the Great Plains
The bison wolf is an endemic subspecies of North America. Endangered. The number of subspecies is about 4000 individuals. It has a multi-colored color (gray-black-brown). Individuals weigh 27-50 kg.
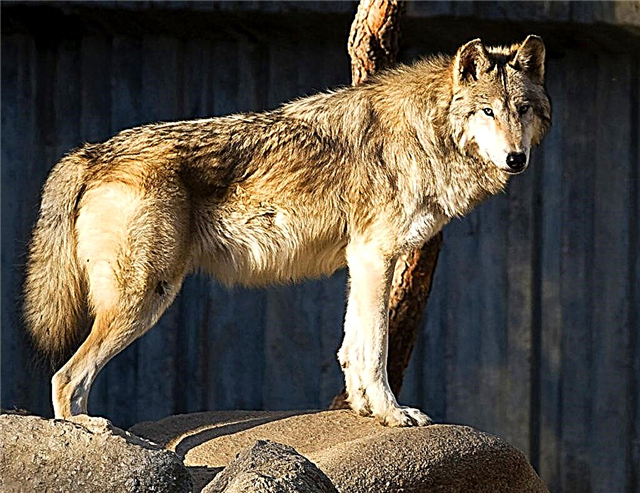

Canadian
Alaskan subspecies is considered the largest among all subspecies of the wolf living in North America. The specimens are quite large: height - up to 91 cm, weight - up to 65 kg. Predators are perfectly adapted to survive in difficult conditions, are able to travel long distances.

Interesting fact: A Canadian wolf can travel about 115 km per day. He has large lungs that allow breathing at high altitude without any problems.
Asian
An Indian / Iranian / Asian subspecies is found in India, Iran, Afghanistan and surrounding countries. It differs in brown color, short and thick coat. Individuals weigh from 25 to 32 kg, and grow up to 75 cm at the withers. Unlike the Arab subspecies, the Asiatic is darker and larger.
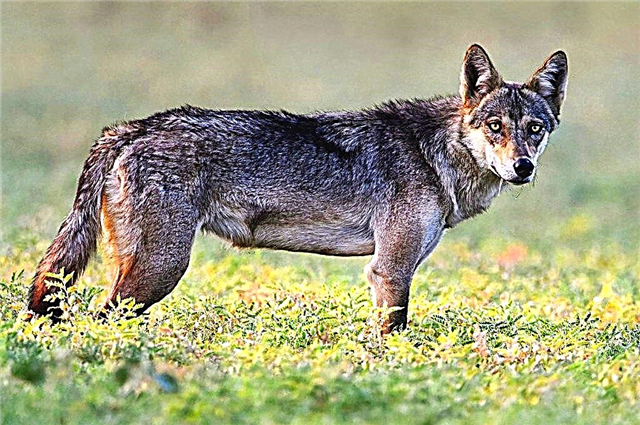

Redhead
The rarest subspecies of the wolf.It has a small size (weight - up to 41 kg, height - up to 79 cm), long legs and ears, short fur. The coat has shades of black, red, and brown. The subspecies lifestyle is similar to an ordinary wolf.
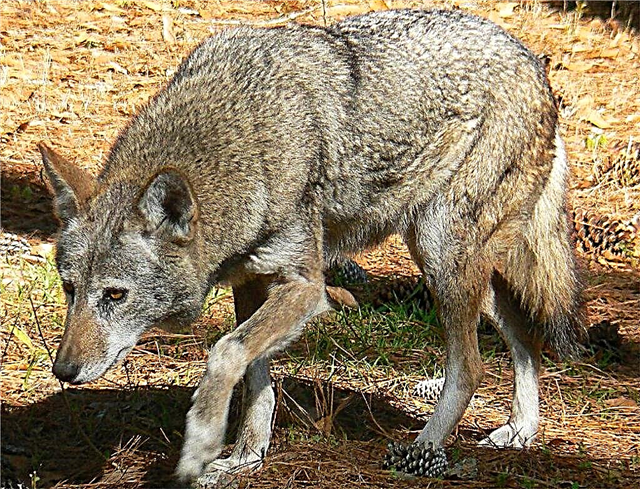

Iberian
Distributed in the forest, lowlands of Spain, Portugal. It is characterized by small size (average weight - about 40 kg). A distinctive feature of the subspecies is the presence of small dark marks, because of which it is called "labeled". Iberian wolves are useful as they control the wild boar population.
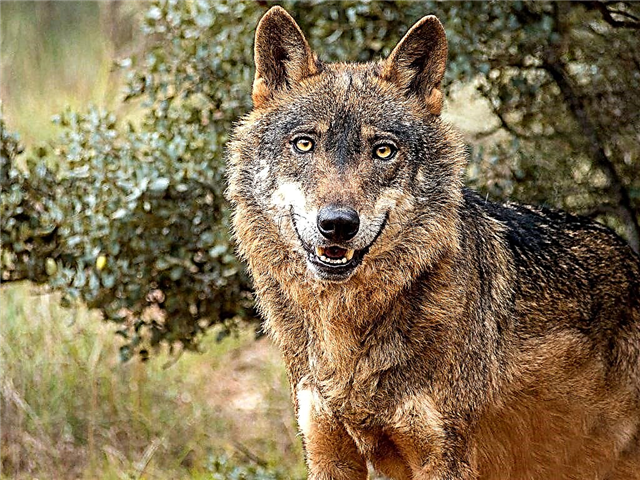

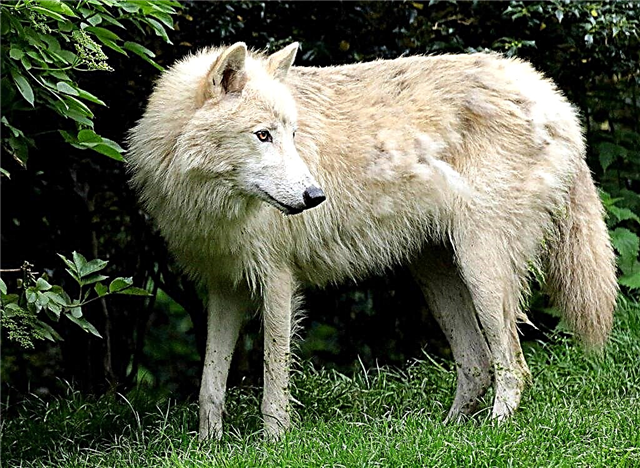
Polar
The range of the subspecies is the Arctic and the tundra zone, except for glaciers. The wolf is perfectly adapted to life in difficult conditions: it withstands low temperatures, dispenses with sunlight, starves for a long time and is generally unpretentious to food. The polar subspecies lives in the pack.

Interesting fact: There is an opinion that the polar wolf is the ancestor of the Samoyed dog - one of the most ancient breeds.
How is a wolf different from a dog?
The wolf is distinguished by stronger and higher legs, large paws, an elongated head. The forehead and muzzle are wider, there is a lot of hair on the sides. In general, the face is much more expressive. For example, scientists were able to identify about 10 emotions that the wolf expresses.
Predator tail is thicker and longer. He does not have a manner of wagging his tail, as dogs do. The lowered tail indicates the calm of the beast, and twitching indicates discontent.

Wolves have thicker, tougher and denser hair. It consists of undercoat and coarse hair. Therefore, the predator is reliably protected from cold, water, and dirt. With the onset of heat, wolves gradually get rid of winter fur, and some can change color.
Another hallmark is traces. The wolf leaves larger prints (8.5-11 cm) than the dog. The two middle fingers protrude more forward, and the lateral fingers are set back. The tracks look more heaped. Predators try to stay farther from people and their dwellings, and dogs, on the contrary, come closer.

How does the wolf howl?
Make a loud howl, the wolf spans a wide range of frequencies. However, a person can only hear high notes, and then they will not be the last. Animals use a variety of sounds to communicate with their pack.
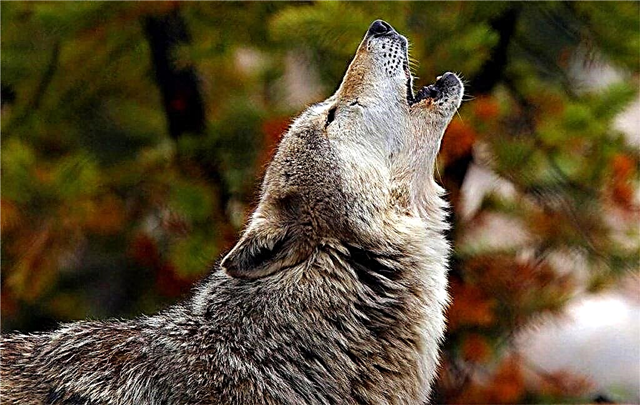

A collective howl indicates a wolf demonstration of belonging to a pack. Possible causes of howling:
- pack gathering;
- the call of females / males;
- protection of caught prey;
- flock warning of danger;
- struggle for territory;
- location indication.
Also, wolves can thus share their personal experiences: report injuries, the birth of offspring, the loss of relatives, etc.
Why does a wolf howl at the moon?
There are many legends and tales about why wolves howl at the moon. However, most scientists are convinced that the moon does not have a significant effect on predators, unlike people and natural phenomena.

On a full moon, a wolf howl can be heard more often, since it is accompanied by a lack of wind, well-lit surroundings. Predators often go hunting at night and when they howl, they raise their heads high up to achieve greater purity and sound volume.
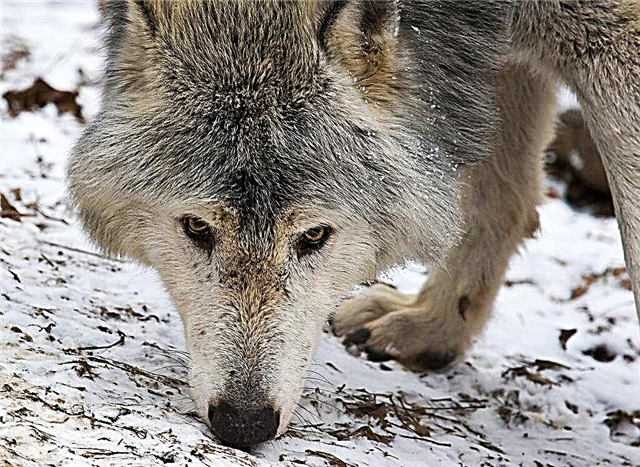
How does a wolf find prey?
The wolf has a well-developed sense of smell - it is able to feel prey at a distance of 3000 m. Animals perfectly distinguish smells and use this to mark the territory. Predators hide the meat left after the hunt, masking it with dirt, like bears. Therefore, it is worth avoiding such "caches" - their owners are probably nearby.

Wolf Pack
The number of flocks is 5-11 individuals on average, it all depends on subspecies and their habits. In this case, adult animals are only a couple. The rest are minors and one year olds. A flock can be formed by several families.
Male and female can mate for 5 years, produce offspring annually. When young individuals become sexually mature and competition occurs, the couple breaks up.
If the pack is already formed, then the outsiders have too little chance of joining it.They can take a young wolf up to 3 years old, which the couple will consider their child. Also, an adult single male is sometimes accepted if the flock needs him.

The flock overcomes about 25 km per day in search of prey. It occupies a territory much larger than what is actually required (about 70 km2) Wolves do this in the event of a change in the amount of prey - this should not affect the survival of the pack.
Predators stay closer to the center of their zone (around 40 km2), so as not to accidentally meet with another flock. They try to avoid such hassles, since in wolf battles 15-65% of individuals are destroyed.
Reproduction and development
Wolves are monogamous animals that create pairs for the long term. In the wild, begin to breed at 2 years of age. In captivity - much earlier, at the age of 9-10 months. It all depends on environmental conditions.
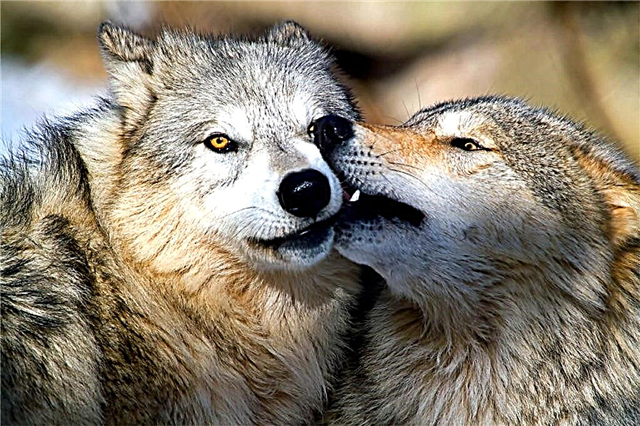

Interesting fact: there are usually more males in the pack, so you can rarely meet a female without a pair.
A she-wolf is capable of giving birth to puppies annually. Pregnancy lasts 62-67 days. At this time, the female does not leave the safe central part of the territory. The number of offspring is higher than that of other canids. Litter usually consists of 5-6 babies.
A newborn wolf cub weighs about 0.5 kg. Initially blind, puppies begin to see 9-12 days later. At the age of 1.5 months, the wolf cubs become quite strong and move freely outside the den.
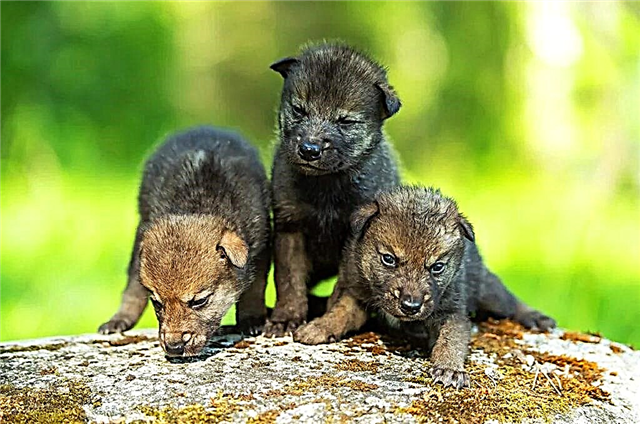

The she-wolf does not leave the den during the first 3 weeks after the birth of the offspring. The male fully provides the family in terms of food and protection. The growth and development of cubs is very fast. At three weeks of age, the wolf cubs play, bite, but painlessly. In the first 5-8 weeks, they fight among themselves - a hierarchy is established.
She-wolf care
Wolves are distinguished by intelligence, learning ability, a variety of emotions. In fact, predators in this regard are very similar to humans. In particular, the she-wolf is the embodiment of an ideal mother who carefully prepares for motherhood.

Stages of maternity in she-wolves
At the initial stage of pregnancy, the she-wolf spends a lot of time with the male, as in the future she will be completely occupied by the offspring. Then the female searches for a suitable place for the lair and equips it. At first, other members of the pack are not allowed to enter, but when the cubs grow up, the whole family will take care of the offspring.
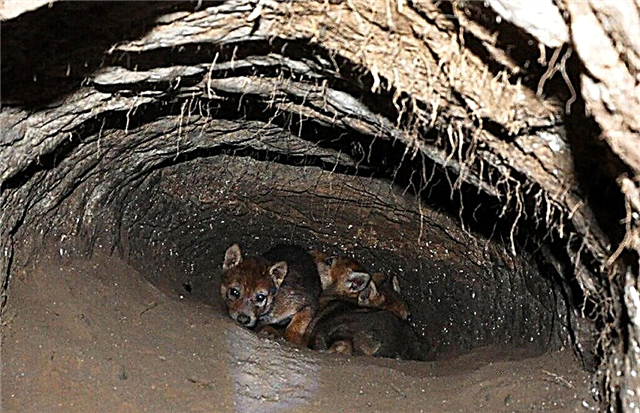

The birth of cubs takes place in a den. The female has innate abilities and knowledge regarding how to behave during childbirth and with offspring. She regularly licks and feeds babies, not leaving alone.
Important characteristic of the she-wolf
A wolf’s mother’s instinct is innate. She takes care of babies in every way. In general, for each female, the birth of offspring is the main goal. The she-wolf is completely disinterested when it comes to her puppies. She may starve for several days and be thirsty, but she will not leave the cubs in danger.

Wolf and hunting
Hunting is often carried out by the whole flock, sometimes by separate individuals. The advantage of predators is the ability to work together, so they are able to defeat the enemy, which is several times larger and stronger.
The hunt is conducted on the occupied territory. Wolves howl call on other members of the pack to hunt. Thus, another's flocks receive a warning. Predators try to go unnoticed for as long as possible. Then comes the chase stage. The hunt lasts until the prey is caught, because this is the key to the successful survival of the flock.
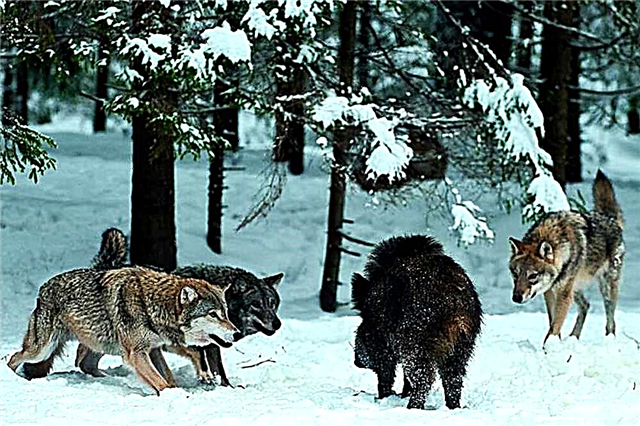

Wolves are afraid of large horned animals, so some individuals can distract prey, while others can surround and attack from all sides. Animals most often eat all caught prey, but they can also leave meat in reserve. Puppies bring food to adults directly into the den.
The benefits of wolves
The wolf is called the "orderly of the forest" and this is its main benefit. Predator is an important part of the ecosystem. It controls the populations of certain animal species, in particular large ungulates.Sick animals cannot escape from wolves and become easy prey. So animals do not allow diseases to spread.

Why is a wolf called a wolf?
It is believed that the name of the animal came from the word "drag." Such an association arose due to the fact that predators dragged the caught prey along with them. In Russian, the word “wolf” appeared from the old Russian “vlk”, and in the Pre-Slavic it looked like “vlk”.

Wolf Ancestors - Evolution
The wolf probably came from the species Canis lepophagus. This is a small predator that lived at least 5 million years ago in North America. Perhaps coyotes also came from him.
Gradually, the ancient wolf increased in size, gained great strength. Scientists have found the fossils of an ancient wolf, whose age was about 1.8 million years. He was much more like a modern predator. The animal was common in Europe.
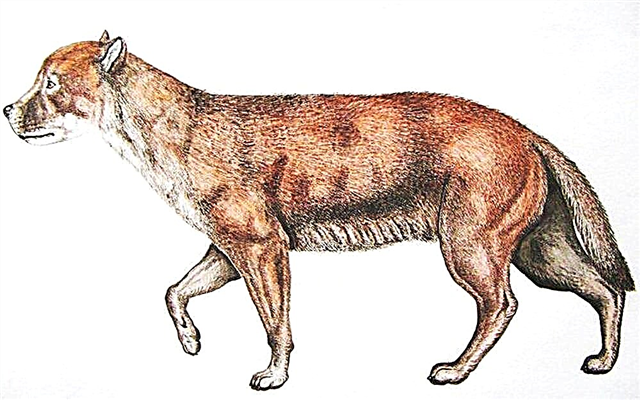
Specialists came to the conclusion that in the family tree of the common wolf there are at least four branches:
- Himalayan line (the most ancient);
- African line;
- Tibetan line;
- indian line.
The terrible wolf, which disappeared about 8,000 years ago, could not stand the competition with the gray, to which hunger was added. Since then, the common wolf has become widespread throughout the world.